


Next: 2.3 Galerkin Discretization
Up: 2. The Finite Element
Previous: 2.1 Poisson Problem
Contents
2.2 The Weak Formulation
The weak formulation of the boundary value problem 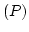 is then obtained by the multiplication of Eq. (2.1) with
is then obtained by the multiplication of Eq. (2.1) with
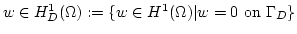 and integration over
and integration over 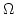 :
:
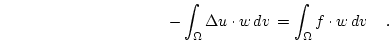 |
(2.4) |
Integration by parts gives
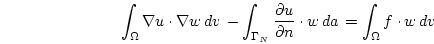 |
(2.5) |
and substitution of the boundary conditions and rearrangement leads to
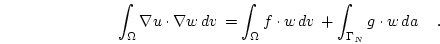 |
(2.6) |
Now we incorporate the (possibly inhomogeneous) Dirichlet boundary conditions
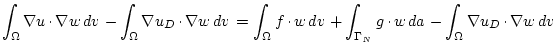 |
(2.7) |
and substitute the homogeneous solution
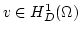 , which is given by
, which is given by 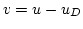 and satisfies
and satisfies 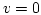 on
on 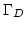 . This gives us the weak formulation of the Poisson problem
. This gives us the weak formulation of the Poisson problem 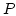 which reads: Find
which reads: Find
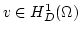 such that
such that
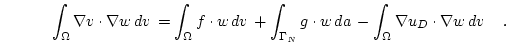 |
(2.8) |



Next: 2.3 Galerkin Discretization
Up: 2. The Finite Element
Previous: 2.1 Poisson Problem
Contents
Werner Scholz
2003-06-08
![]() is then obtained by the multiplication of Eq. (2.1) with
is then obtained by the multiplication of Eq. (2.1) with
![]() and integration over
and integration over ![]() :
: